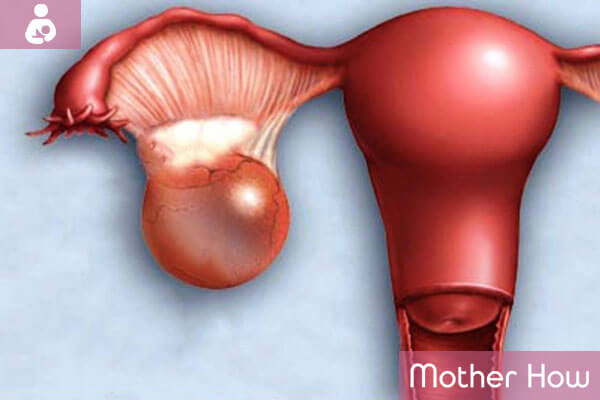
An ovarian cyst is a protrusion with a liquid that is formed mainly of the follicle on one or both ovaries. Anatomically cyst looks like a thin-walled cavity in the form of a bag. The size may vary from a few centimeters up to 15-20 centimeters in diameter. The cyst appears to be rather functional or follicular in 90 percent of the cases. Its formation is caused by the over-ripening of the follicle where the female sex cell is developing. Every menstrual cycle one out of two ovaries produces one ovum which should head towards the fallopian tube from the follicle. The latter in its turn becomes a corpus luteum and produces progesterone. That is the main idea of ovulation.
The cyst forms in the case when the follicle is not ruptured but remains in the ovary and is filled with liquid. Sometimes its sizes begin to cause discomfort blocking the fallopian tube. But in most cases, a follicular cyst is resolved during the next menstrual cycle without leaving any traces. The functional cyst may also be caused by the widening of the corpus luteum. It is formed similarly and is called a corpus luteum cyst.
Another variant of the functional cyst is the hemorrhagic cyst. It takes place when the blood vessels inside the follicle or corpus luteum are ruptured. Then the bleeding accompanied by pain may be observed. Also, the dysontogenetic cyst exists, which may appear due to a violation of the growth and development of the ovaries during puberty. The so-called cyst tumor that may lead to ovarian cancer is another variation of the disease.
Symptoms of the Ovarian Cyst
Most of the time cyst does not show and reduces in size until it disappears in the next few menstrual cycles. It may be diagnosed during the ultrasound diagnostics of organs of the smaller pelvis. Only in rare cases, symptoms may be observed. The symptoms of the ovarian cyst include acute pain in the lower stomach, pressure in the pelvis, prolonged pain during menstruation, violated menstrual cycle (irregular), vomiting after intensive training or sexual contact, high pressure during emptying of the bladder or rectum, vaginal pain accompanied with bleeding.
There are also symptoms that together with those previously mentioned indicate the necessity to visit a hospital. Those are body temperature above 38 degrees, weakness, and dizziness, plentiful secretion during menstruation, the increase of stomach in size, facial hair growth similar to that of male, thirst, and copious urination, abnormal arterial pressure, rapid loss of weight, the consolidation in the abdominal area.

Ovarian Cyst Examination and the Diagnosing
In order to diagnose the kind of pathology, the following procedures are performed: Computer tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, transvaginal ultrasound examination, laparoscopy with a preceding removal of the cyst (if found), hormonal analyzes (FSH and LH, estrogen, testosterone). Also, Douglas puncture of the rear vaginal vault in case there is a suspicion of internal bleeding that could have been caused by rupture of the cyst can be performed.
Analyses for tumor marker CA-125 to exclude the variant of ovarian cancer are also necessary. A pregnancy test is also obligatory, but not because the treatment for those who are pregnant and for those that are is different. The ectopic pregnancy may have similar symptoms with an ovarian cyst.
Causes of Ovarian Cyst
Unfortunately, the physiological mechanisms of ovarian cyst occurrence are not completely examined yet. Most physicians consider that such pathology can be caused by hormonal failure, inflammatory processes, and apoptosis (programmed death of the cells). According to statistics, ovarian cyst affects about 7 percent of adult women (even after menopause).
The occurrence of such disease is connected with the menstrual cycle and does not depend on the age and general condition of females’ health. That is why the ovarian cyst rarely takes place after menopause. However, the influence of the cyst on the female body is various and depends on many factors.
For example, cysts that appeared due to the consumption of ovarian stimulators will completely disappear without any consequences during the next few menstrual cycles. In cases when the cyst is accompanied by risk factors such as stress, sexual infections, artificial pregnancy abortion, obesity, smoking, early menarche, late menopause – there are possible consequences. Those also include tumors, reduction of reproductive function, and even infertility or miscarriage.
Therefore, we may conclude that the risk of cyst increases in case of irregular menstrual cycles, the early beginning of menstruations (before the age of eleven), hormonal disorders (hypothyroidism), the occurrence of the cyst in the past. Also, such factors as treating breast cancer with tamoxifen and surgeries on the system of the reproductive organs in the past as well as smoking, obesity, and infertility can cause ovarian cyst.

Can a Woman get Pregnant in Case of Ovarian Cyst?
In general, the reproductive function is not violated due to an ovarian cyst. More than that the pregnancy contributes to the rapid disappearance of the pathology. The cyst rarely appears during pregnancy as the follicles are usually not formed. But if there is a cyst in the ovaries and you are willing to get pregnant there are some factors to be considered. As it was previously mentioned the cyst is the consequence of the absence of ovulation.
The follicle that is turned into a cyst does not allow the ovule to enter the fallopian tubes, cluttering the ovule and not allowing the other follicles to develop. That is why if there are difficulties with conceiving a child the examination on the subject of the presence of cysts may help to figure out the problem. Normally such a cyst is regressing during the next 2-3 menstrual cycles and the pregnancy becomes possible.
However, the constant observation of the doctor is required if the woman of reproductive age has: a cyst bigger than 8 centimeters in diameter, the absence of the regression of the cyst, the increased content of the tumor marker CA-125. In such cases the laparoscopy is necessary. The removed cyst is sent to histological analysis. But before that, gastroscopy, abdominal ultrasound diagnostics, colonoscopy differentiate the ovarian cyst from other possible pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and other abdominal organs.
But returning to cases of pregnancy during the ovarian cyst ( should be held in mind that the cyst of the corpus luteum is normal for that state and all the previously mentioned is not connected with that variation) The observation of patients in such cases shows that about 4 percent of them required surgeries. The problem is that the cyst leg is twisted and the cyst may rupture due to the pressure caused by the growth of the fetus. To avoid such consequences it is necessary to visit a gynecologist before getting pregnant.
Conclusion
Thus, it appears that an ovarian cyst is a common enough pathology that can be either removed or disappear without a trace by itself. An ovarian cyst is not a problem for pregnancy in most cases.

Born in Belarus, 1985, a pedagogue and family psychologist, mother. Taking part in procedures of social adaptation of the foster children in new families. Since 2015 is a chief editor of the motherhow.com project, selecting the best and up-to-date material for those, who are planning, expecting, and already having babies.